What Is DevSecOps?
As organizations rapidly deploy both AI-generated and human-written code, traditional security approaches struggle to ensure that software is developed both securely and efficiently. That’s why more teams are turning to DevSecOps. And according to security leaders, it’s paying off, a Gartner survey found that 66% of organizations that have implemented or are in the process of implementing DevSecOps report experiencing fewer security incidents.
DevSecOps isn’t just a trend, it’s a strategy that integrates development, security, and operations into a single, streamlined process. By embedding security into every phase of the software lifecycle, it enables faster delivery, tighter collaboration, and more effective risk management. From SAST and DAST to continuous integration and regular penetration testing, DevSecOps transforms security from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.

The Difference Between DevOps and DevSecOps
Let’s talk first about the differences between DevOps and DevSecOps. DevOps combines “Development” and “Operations” to bridge the gap between software development and IT operations.
In the past, these areas often worked separately, resulting in communication barriers, slow delivery cycles, and limited collaboration. DevOps breaks down these barriers and promotes a culture of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement.
What is SecOps?
On the other hand, DevSecOps is the integration of security throughout the entire development process. SecOps stands for “Security Operations,” its purpose is simply to implement and manage security practices and processes to properly secure an organization. The main purpose of SecOps is to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, monitor systems for potential threats, and respond to security incidents in a timely and effective manner.
Some security measures employed in SecOps are vulnerability scanning, penetration testing (or even better PTaaS), and incident response planning. By adopting SecOps practices, organizations enhance their security posture, reduce the likelihood of breaches, and minimize the impact of security incidents.
The Result of Embracing DevSecOps
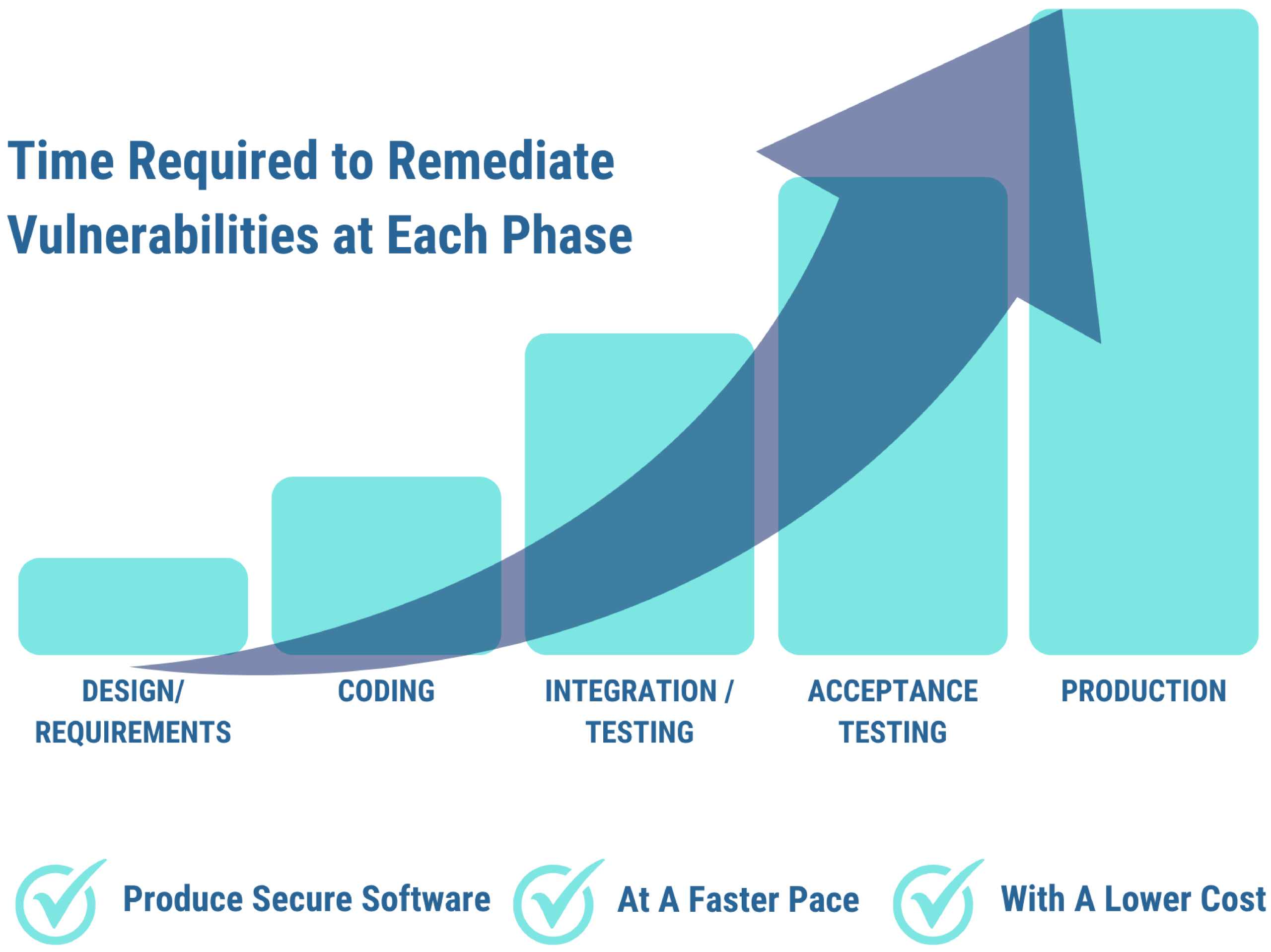
DevSecOps embeds security practices into every stage of the development and operations lifecycle, making it possible to identify and remediate vulnerabilities early when fixes are faster and more cost-effective. This “shift-left” approach ensures that security is considered from the very beginning, starting with planning and design, and continues through development, testing, deployment, and beyond.
By merging the principles of DevOps and SecOps, DevSecOps strikes a critical balance between speed, agility, and security. It encourages close collaboration between developers, operations teams, and security professionals to identify risks, apply secure coding practices, run continuous security tests, and monitor for emerging threats.
This integration builds security into applications from the ground up, resulting in more resilient software and a stronger overall security posture. It also fosters a culture of shared responsibility, breaking down silos and improving communication between traditionally separate teams.
Ultimately, DevSecOps enables organizations to deliver high-quality software at speed, without compromising on security. When implemented effectively, it empowers IT professionals across disciplines to collaborate, innovate, and build with confidence.

Download Your Guide to DevSecOps
Learn how you can integrate security into the entire SDLC through DevSecOps, resulting in your organization producing more secure software, at a faster pace, cost-effectively.
DevSecOps Process

The DevSecOps process brings security into the heart of modern software development by embedding it directly into each phase of the DevOps lifecycle. Rather than treating security as a separate step or final checkpoint, DevSecOps ensures it’s woven into every stage, from initial coding to deployment and ongoing monitoring.
The process outlined in the diagram illustrates how development, security, and operations are continuously integrated to create a seamless, secure pipeline. Each stage plays a vital role in reducing risk, improving agility, and delivering resilient software at scale.
Every secure application begins with a well-structured plan. This phase involves defining requirements, setting objectives, and identifying potential security risks before development begins. Security is embedded by conducting threat modeling, establishing security acceptance criteria, and aligning compliance goals with development timelines. Collaboration between developers, security teams, and stakeholders ensures that security is treated as a priority from the outset.
In the coding phase, developers write application code guided by secure coding best practices. Security tools such as Static Application Security Testing (SAST) are used to scan for vulnerabilities in real-time. Code reviews, linting, and peer collaboration are reinforced with automated checks to prevent the introduction of insecure code.
As code is compiled and applications are packaged, this stage verifies integrity and security at the build level. Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools check for known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies. Security policies are enforced to ensure only verified, compliant components make it into the build.
Security and functional testing are both critical during this stage. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools simulate real-world attacks on running applications, while manual testing, fuzzing, and penetration testing (or PTaaS) are used to uncover more complex vulnerabilities. Testing environments mirror production as closely as possible to ensure accuracy.
Before code moves to production, the release phase ensures all approvals, security gates, and compliance requirements are met. Security checks are automated to reduce friction, while tools like container scanning and image signing validate that deployments are secure and untampered.
Secure deployment ensures applications are rolled out in a controlled and reliable way. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scanning, policy enforcement, and configuration validation help prevent misconfigurations that could expose the environment. Continuous deployment pipelines are hardened with identity management and role-based access controls.
Once deployed, applications are monitored for health, performance, and security. This phase includes log aggregation, anomaly detection, and runtime protection. Security teams manage updates, patching, and policy enforcement across systems to ensure continuous protection.
The final stage focuses on ongoing visibility and threat detection. Security teams use SIEMs, threat intelligence feeds, and behavioral analytics to detect and respond to suspicious activity. Insights gained here inform future planning and help continuously improve the overall security posture.
Common DevSecOps Practices
Each stage of the DevSecOps process contains a collection of integrated practices that bring security into every phase of the software development lifecycle. These practices ensure that security is continuous, automated where possible, and collaborative by design. While implementation can vary depending on the organization’s maturity and toolsets, several foundational practices are shared across successful DevSecOps programs:
Threat Modeling & Risk Assessments
Before code is written, security teams and architects collaborate to identify potential threats, system entry points, and abuse scenarios. This proactive approach helps prioritize controls based on business impact and known attack vectors. Threat modeling sessions inform architectural decisions, while formal risk assessments ensure alignment with regulatory and organizational risk tolerance.
Stage of DevSecOps: Plan
Secure Coding Standards
Developers adhere to secure coding guidelines that reduce the risk of common vulnerabilities like SQL injection, XSS, and buffer overflows. These standards are embedded in the development culture through documentation, training, and enforcement. Real-time IDE integrations and code linters provide immediate feedback, reducing the cost of remediation and improving baseline code quality.
Stage of DevSecOps: Code
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
SAST tools scan the application’s source code, bytecode, or binaries without executing them. By analyzing the code early, SAST identifies vulnerabilities like hardcoded secrets, improper error handling, or logic flaws. These tools are integrated into CI/CD pipelines to automatically scan every commit, merge, or pull request.
Stage of DevSecOps: Code
Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
SCA tools monitor third-party libraries and dependencies for known vulnerabilities, outdated versions, and license risks. With the widespread use of open-source components, SCA provides critical visibility into your software supply chain and alerts teams when components need to be patched or replaced.
Stage of DevSecOps: Build
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
DAST tools analyze running applications to detect issues that manifest at runtime, such as insecure session handling, authentication bypass, or cross-site scripting. These black-box tests emulate external attacks without requiring access to source code, helping teams uncover vulnerabilities that SAST can’t reach.
Stage of DevSecOps: Test
Penetration Testing and PTaaS
Manual penetration testing, especially when delivered continuously through Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS), goes beyond surface-level scans to uncover complex vulnerabilities, business logic flaws, and chained exploits that automated tools routinely miss. The result is faster resolution of high-risk issues, better alignment with development cycles, and a measurable reduction in exploitable vulnerabilities over time.
Stage of DevSecOps: Test
Container & Image Scanning
Before software is released, container images are scanned for embedded secrets, outdated packages, misconfigurations, and known vulnerabilities. Image signing and scanning tools ensure the integrity and security of your containers from build to deployment.
Stage of DevSecOps: Build, Release, Deploy
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security
IaC templates (Terraform, CloudFormation, etc.) are scanned for insecure defaults, overly permissive access, and misconfigured resources. By securing infrastructure definitions before deployment, teams reduce the risk of exposed cloud services, identity mismanagement, and data leakage.
Stage of DevSecOps: Deploy
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) & Identity Enforcement
Secure deployment also depends on proper identity and access controls. RBAC policies ensure that only authorized users and systems can access deployment pipelines, secrets, and critical infrastructure. Identity validation tools integrate with CI/CD workflows to prevent privilege misuse.
Stage of DevSecOps: Deploy
Continuous Monitoring & Runtime Protection
Once in production, applications and infrastructure must be monitored for suspicious behavior. Tools like EDR, XDR, or application-level RASP provide visibility into anomalous behavior, policy violations, and attacks in progress. This layer helps prevent zero-day exploits and rapidly evolving threats.
Stage of DevSecOps: Operate
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) & Threat Intelligence
SIEM platforms aggregate logs from across systems, correlate them against known threat patterns, and generate alerts for investigation. When combined with external threat intelligence feeds and behavior analytics, this enables faster detection and more informed incident response.
Stage of DevSecOps: Monitor
By adopting these practices, organizations not only reduce the likelihood of security incidents but also create a culture of shared responsibility where security becomes an enabler of innovation, not a barrier.
The Importance of a Cultural Shift
Implementing DevSecOps effectively requires a cultural shift within organizations, moving away from traditional siloed roles to a collaborative, security-centric approach. This shift views security as a shared responsibility across all teams, integrating it from the outset of the software development lifecycle.
By embedding security early, everyone becomes involved in safeguarding the system, enhancing the overall security posture. The shift also emphasizes continuous learning, adapting to new threats with regular training and awareness initiatives. This not only bolsters security but also aligns development processes with broader business objectives, resulting in more secure, agile, and high-quality software outputs.
How TrollEye Can Help
At TrollEye Security, we help organizations turn DevSecOps from a concept into an operational reality. Our DevSecOps services are designed to integrate seamlessly into your development workflows, bringing together expert guidance, continuous testing, and strategic alignment across teams. From secure coding and vulnerability scanning to continuous penetration testing and infrastructure hardening, we embed security into every stage of your software delivery pipeline.
Whether you’re just getting started or scaling an existing program, we work side-by-side with your developers and engineers to build a sustainable security strategy that aligns with your tools, team structure, and release cadence. The result is faster delivery, fewer vulnerabilities, and a stronger security posture across every release.
With TrollEye, DevSecOps isn’t just about shifting left, it’s about moving forward with confidence.
FAQs About DevSecOps
What is DevSecOps?
DevSecOps blends Development, Security, and Operations, integrating security into every phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). It ensures secure code is delivered faster by shifting security “left”, from planning through deployment, rather than treating it as an afterthought.
What does the DevSecOps process look like?
The DevSecOps process weaves security throughout the entire software development lifecycle, ensuring that protections are considered from the very beginning rather than after deployment. It typically follows a sequence that starts with planning and coding, moves through building, testing, and releasing, and continues with deployment, operations, and ongoing monitoring. At each stage, security practices such as code reviews, automated testing, compliance checks, and runtime monitoring are embedded into the workflow.
What kinds of security tools or practices are embedded in DevSecOps?
DevSecOps emphasizes a wide range of practices that span from the earliest design phases to live production environments. Threat modeling can be used during planning to anticipate risks before code is written. Static analysis tools review code for vulnerabilities before deployment, while dependency scanning helps identify issues in third-party components. By blending these approaches, DevSecOps creates a feedback loop where security becomes a natural part of everyday development work.
What are the biggest challenges with DevSecOps implementation?
According to Gartner, the top issues organizations experience with DevSecOps implementation are: difficulty implementing testing tools (60%), cloud-related complexity (57%), and difficulty with integrations (51%).
What tangible results can DevSecOps deliver?
According to Gartner, 66% of organizations adopting DevSecOps report fewer security incidents. By embedding testing and monitoring throughout the development lifecycle, teams catch vulnerabilities earlier, reduce remediation costs, and release software more reliably. The result is stronger security and faster delivery without sacrificing quality.



